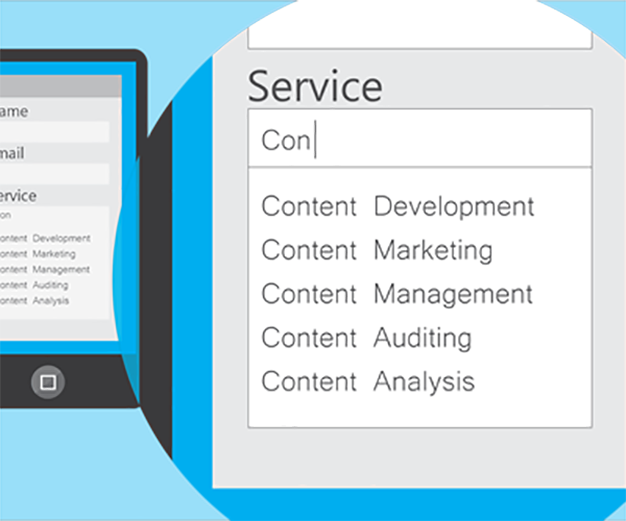
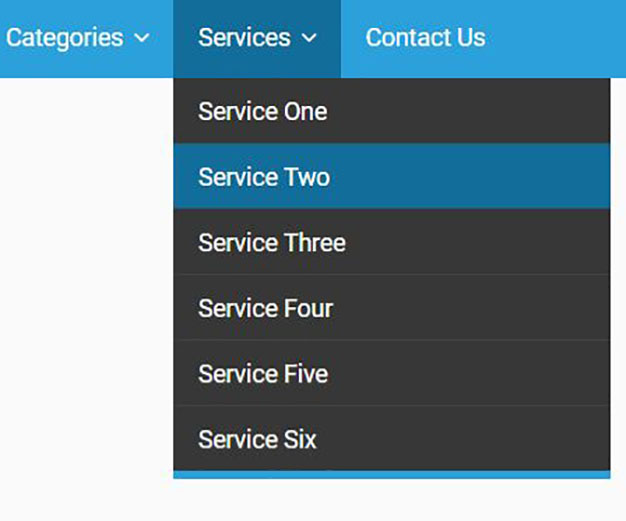
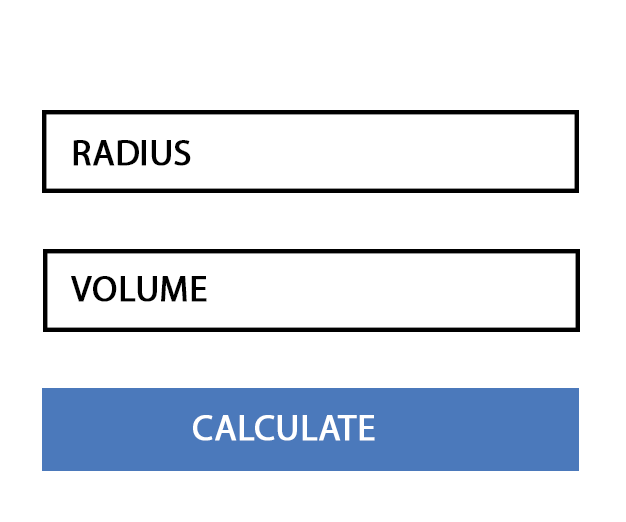
Document Object Model
The Document Object Model (DOM) connects web pages to scripts or programming languages by representing the structure of a document—such as the HTML representing a web page—in memory. Usually that means JavaScript, although modelling HTML, SVG, or XML documents as objects is not part of the JavaScript language, as such.